The path to a carbon positive future


· 10 min read
This article is part of our series to spread free & quality sustainability knowledge for all. Compare on Data Hub™ the sustainability performance of companies driving a carbon-positive future: Ørsted, Enel and Unilever.

In carbon emissions lingo, carbon positive is a term used to describe an entity that removes more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than it emits. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as planting trees, investing in renewable energy, or using carbon capture and storage technology. While the concept of being "carbon neutral" has gained significant attention in recent years, there is an emerging movement that goes beyond mere neutrality, aiming to actively remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and restore the delicate balance of our ecosystems. This groundbreaking approach is known as "carbon positivity," and it promises to revolutionize our efforts in the fight against climate change. In this article, we delve into the concept of carbon positivity, exploring its potential, its challenges, and the remarkable possibilities it holds for building a sustainable future.
In 2021, annual global CO2 emissions reached 37.9 gigatonnes, following a 5.3% decrease in 2020. This stat shows that the task of reducing the emission of carbon and other greenhouse gases is still work in progress. Carbon positivity is based on the notion that we can’t only curb carbon emissions; we can go a step further and remove more than we emit. Let’s take a look at some of the important reasons for curbing carbon emissions.
Curbing carbon emissions is crucial for stabilizing the Earth's climate. Since 1990, global CO2 emissions have increased by over 60 percent. The excessive emission of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions are the primary driver of global warming. In addition, increasing levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) in Earth’s atmosphere have led to the acidification of the oceans.
By reducing these emissions, we can mitigate the rate of temperature rise, limit the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, reduce the acidity of our oceans, and protect vulnerable ecosystems and communities from the devastating impacts of climate change.
Carbon emissions are closely linked to air pollution, which poses significant risks to human health. Fossil fuel combustion releases harmful pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide, which contribute to respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and other health issues. By curbing carbon emissions and transitioning to cleaner energy sources, we can improve air quality, promote public health, and enhance the overall well-being of present and future generations.
Addressing carbon emissions presents an opportunity to foster sustainable economic growth. Investing in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and low-carbon technologies not only helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also drives innovation, job creation, and economic resilience. By transitioning to a low-carbon economy, we can unlock new markets, attract investments, and build a more sustainable and competitive future while minimizing the risks associated with fossil fuel dependency and volatile energy prices.
Recognizing the importance of curbing carbon emissions can pave the way for a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable world for ourselves and future generations. It is an essential step towards mitigating climate change, protecting our well-being, and fostering a thriving economy that works in harmony with the environment.

As the urgency to combat climate change grows, concepts like "carbon positive" and "carbon neutral" have gained prominence in sustainability discussions. While both terms relate to reducing carbon emissions, they represent different approaches and levels of ambition in addressing the climate crisis. Here, we delve into the details to understand the distinctions between carbon positive and carbon neutral.
 Being carbon neutral entails achieving a balance between the amount of carbon dioxide emitted and the amount removed from the atmosphere. It involves calculating an organization's or individual's carbon footprint by measuring their greenhouse gas emissions across various activities, such as energy consumption, transportation, and production. To achieve carbon neutrality, emissions are either reduced or eliminated altogether, and any remaining emissions are offset through activities that remove or reduce carbon, such as investing in renewable energy projects or supporting reforestation initiatives. The aim is to ensure that the overall impact on the climate is neutral, with no net increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
Being carbon neutral entails achieving a balance between the amount of carbon dioxide emitted and the amount removed from the atmosphere. It involves calculating an organization's or individual's carbon footprint by measuring their greenhouse gas emissions across various activities, such as energy consumption, transportation, and production. To achieve carbon neutrality, emissions are either reduced or eliminated altogether, and any remaining emissions are offset through activities that remove or reduce carbon, such as investing in renewable energy projects or supporting reforestation initiatives. The aim is to ensure that the overall impact on the climate is neutral, with no net increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
In contrast, carbon positivity goes beyond carbon neutrality by actively removing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than is emitted. It involves actively seeking out strategies and technologies that not only reduce emissions but also help in removing additional carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in a long-term, secure manner. Carbon positive initiatives often employ nature-based solutions, such as reforestation, afforestation, or restoring degraded ecosystems, which act as carbon sinks and absorb more carbon dioxide than they release.
Additionally, carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, direct air capture, and enhanced mineralization are innovative approaches being explored to achieve carbon positivity. The objective of being carbon positive is to contribute to a net reduction in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and help reverse the impacts of climate change.
While carbon neutrality focuses on offsetting emissions and achieving a balance, carbon positivity sets a higher bar by actively reversing the carbon equation. By removing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than is emitted, carbon positivity has the potential to make a significant and lasting impact on global carbon levels. It offers an opportunity not only to address the urgent need to reduce emissions but also to restore the planet's carbon balance and mitigate the effects of climate change.
In summary, carbon neutrality aims to achieve a balance between emissions and removals, whereas carbon positivity strives to go beyond balance and actively remove more carbon dioxide than is emitted. While both approaches contribute to mitigating climate change, carbon positivity holds the potential to create a net reduction in atmospheric carbon levels and drive meaningful, long-term change. As the world grapples with the climate crisis, understanding the difference between these concepts is crucial for setting ambitious sustainability goals and implementing effective strategies to combat global warming.
Becoming carbon positive involves actively reducing your carbon emissions and implementing strategies to remove more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than your activities generate. Here are some steps to guide you on the path toward carbon positivity:
Start by understanding your carbon emission status. Calculate your carbon footprint by identifying emission sources such as energy consumption, transportation, waste management, and supply chains. Use available tools and methodologies to measure and quantify your emissions accurately.
Implement strategies to reduce your carbon emissions as much as possible. This can include improving energy efficiency, transitioning to renewable energy sources, optimizing transportation logistics, adopting sustainable practices in production or operations, and minimizing waste generation. Set ambitious emission reduction targets and develop action plans to achieve them.
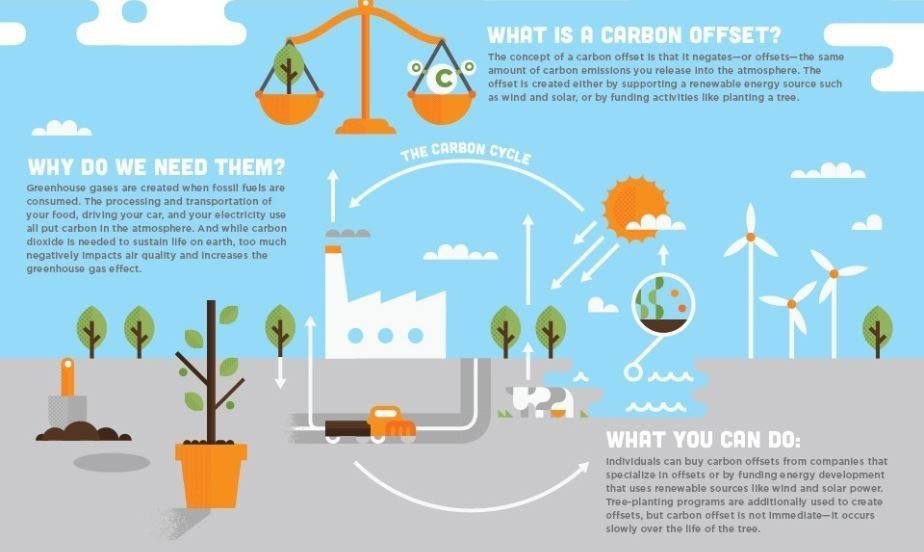
Even with substantial emission reductions, it may be challenging to eliminate all emissions entirely. Offset the remaining emissions by investing in credible carbon offset projects. These projects can include activities like forest conservation or restoration, renewable energy installations, or projects that capture and store carbon dioxide. Ensure that the offsets are verified and meet recognized standards, such as the Verified Carbon Standard or the Gold Standard.
Embrace nature-based solutions to actively remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Planting trees to halt deforestation, restoring degraded ecosystems, or supporting initiatives that enhance soil carbon sequestration can contribute to carbon positivity. Partner with organizations or projects that specialize in these nature-based solutions and ensure they align with recognized standards.
Explore emerging technologies that can help remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This can include carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, direct air capture, or enhanced mineralization. Stay informed about advancements in carbon removal technologies and assess their feasibility and effectiveness for your specific context.
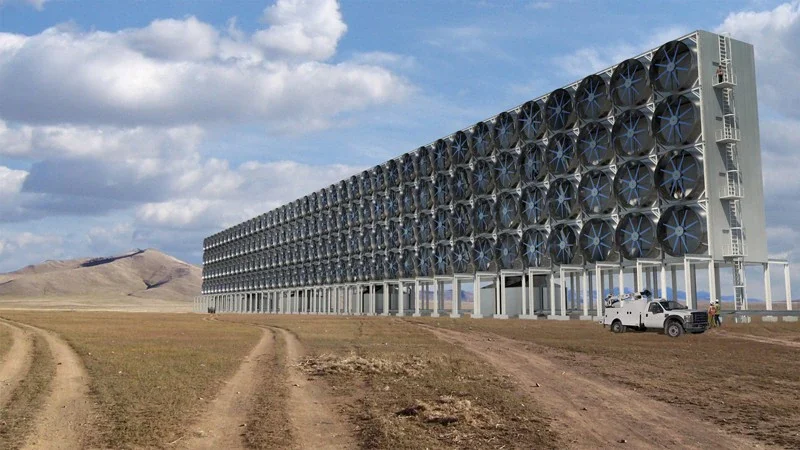

Collaborate with other organizations, industry peers, and stakeholders to amplify your impact. Share best practices, collaborate on carbon reduction initiatives, and support policy advocacy for stronger climate action. Engage with suppliers, customers, and employees to create awareness and promote sustainable practices throughout your value chain.
Becoming carbon positive requires a comprehensive and holistic approach that combines emission reductions, offsetting, nature-based solutions, and embracing innovative technologies. It requires a long-term commitment to sustainable practices and ongoing efforts to continually improve and innovate.
Carbon positive refers to a state where an entity goes beyond achieving net zero carbon emissions by actively removing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than it emits. It involves implementing measures to reduce carbon emissions and adopting strategies that result in a net reduction of atmospheric carbon levels. In other words, being carbon-positive means making a tangible contribution to combating climate change by actively working towards a carbon-negative state.
According to EARTH.ORG, Bhutan is the first carbon-negative country in the world. The country has extensive forests, covering 70% of the land. Thus, the Kingdom can absorb more carbon dioxide than it produces.
illuminem's Data Hub™ tracks companies such as Ørsted, Enel and Unilever. These leaders are removing more carbon from the atmosphere than they emit, with Ørsted and Enel focusing on renewables and Unilever integrating carbon-positive practices.
A climate-positive business is a business that impacts the environment positively. Such a business doesn’t stop at achieving net-zero GHG emissions. They go further to create an environmental benefit by removing additional carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This means such a business doesn’t rest on its oars after achieving net zero emissions; it does more.
The concept of carbon positivity represents an important leap forward in our efforts to combat climate change and create a sustainable future. When we actively remove more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than we emit, we go beyond mere neutrality and strive for a net reduction in atmospheric carbon levels. This ambitious approach requires a combination of emission reduction measures, carbon offsetting, nature-based solutions, and innovative technologies.
Carbon positivity holds the potential to reverse the impacts of climate change and restore the delicate balance of our ecosystems. It presents an opportunity not only to mitigate the effects of global warming but also to foster innovation, drive economic growth, and improve public health. Embracing carbon positivity is a critical step towards building a resilient and thriving planet for current and future generations, ensuring a sustainable and harmonious coexistence with our environment.
illuminem's Data Hub™ tracking sustainability performance data of companies driving a carbon-positive future: Ørsted, Enel and Unilever.
EDGAR - The Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research. (n.d.). https://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu/report_2022
Nguyen, L. (2022). Bhutan: The First Carbon Negative Country In The World. Earth.Org. https://earth.org/bhutan-carbon-negative-country/
Statista. (2023, May 8). Annual global emissions of carbon dioxide 1940-2022. https://www.statista.com/statistics/276629/global-co2-emissions/
Sulfur Dioxide Effects on Health - Air (U.S. National Park Service). (n.d.). https://www.nps.gov/subjects/air/humanhealth-sulfur.htm
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. (n.d.). Ocean Acidification. https://www.whoi.edu/know-your-ocean/ocean-topics/how-the-ocean-works/ocean-chemistry/ocean-acidification/
illuminem briefings

Architecture · Carbon Capture & Storage
illuminem briefings

Carbon Market · Public Governance
illuminem briefings

Carbon · Environmental Sustainability
Financial Times

Carbon Market · Public Governance
GB News

Carbon · Sustainable Mobility
The Scotsman

Carbon Capture & Storage · Public Governance