Rising chance of El Niño sparks concern for heat records


· 2 min read
🗞️ Driving the news: The UN warns that the probability of an El Niño weather event occurring has increased, likely leading to higher global temperatures and heat records
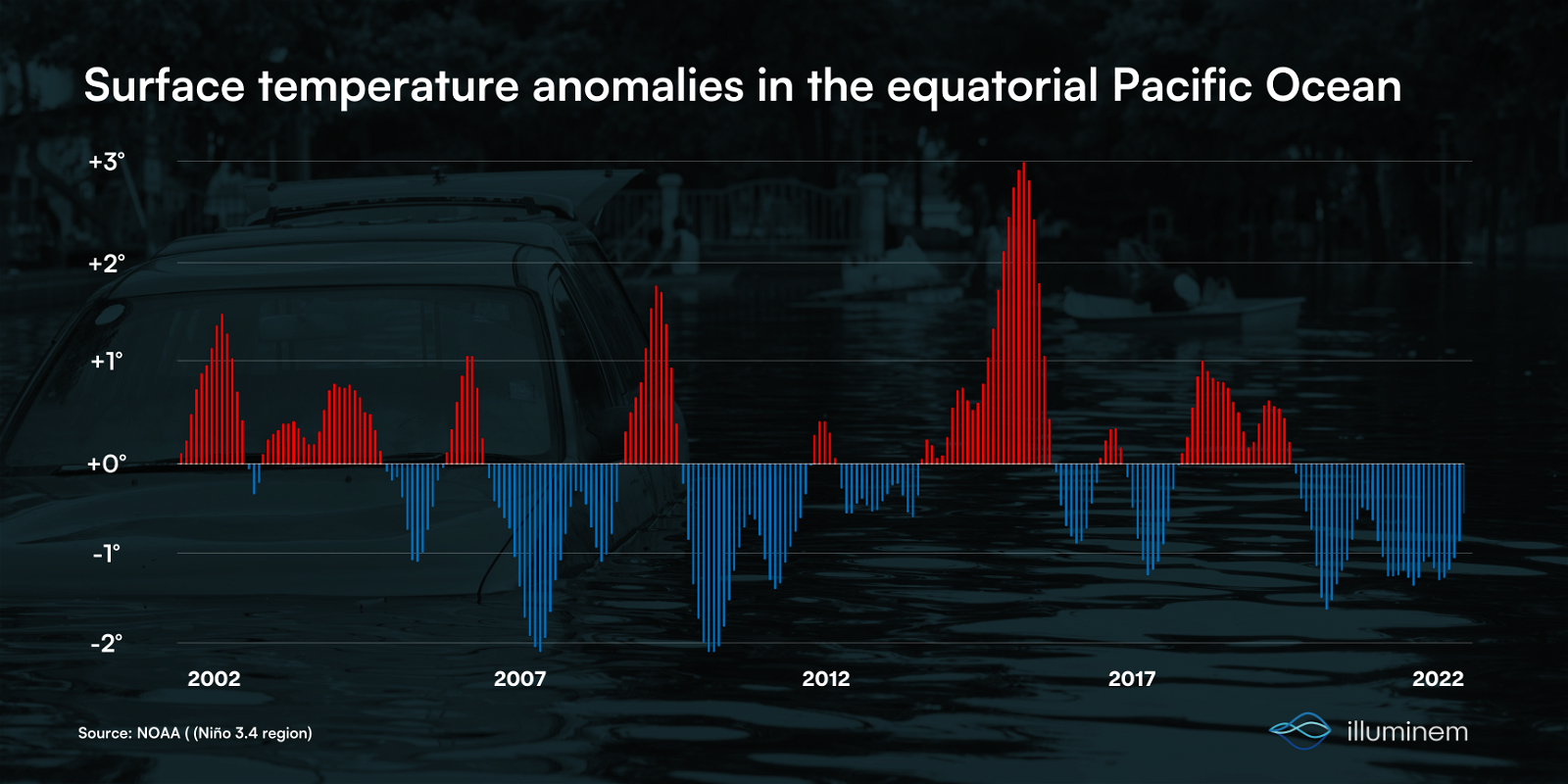
🔭 Science 101: El Niño is a climate pattern that typically occurs every few years in the tropical Pacific Ocean
🌎 Why it matters for the planet: The development of El Niño is significant because it can exacerbate global warming and lead to extreme weather events
⏭️ What next: In the coming months, The WMO and national meteorological services will closely monitor the development of El Niño and the related impact on global temperatures and weather patterns
💬 One quote: "We are expecting in the coming two years to have a serious increase in the global temperatures" (Wilfran Moufouma Okia, Head of the WMO’s regional climate prediction services division)
Click for more on climate change
illuminem briefings

Labor Rights · Climate Change
Steven W. Pearce

Adaptation · Mitigation
illuminem briefings

Climate Change · Environmental Sustainability
Politico

Public Governance · Climate Change
Mongabay

Climate Change · Environmental Rights
El Pais

Effects · Climate Change