Why plant-based milk is better for the environment than dairy milk


· 3 min read
Dairy production is a major contributor to environmental degradation, mainly due to the large amount of land required for raising cows and cultivating feed.
A sizeable portion of the land currently used for dairy farming has the potential to be used for reforestation or other carbon sequestration techniques. Furthermore, the adoption of plant-based milk production practices can play a crucial role in protecting natural habitats and ecosystems. According to estimates, 38% of the planet’s surface is made up of agricultural land. Out of this vast area of farmland, one-third is used for raising livestock, while the remaining two-thirds are made up of meadows and pastures used for grazing livestock.
Large-scale dairy farming frequently requires the clearing of forests and other natural ecosystems to make way for crops that will be used as animal feed. This can have a negative impact on biodiversity.
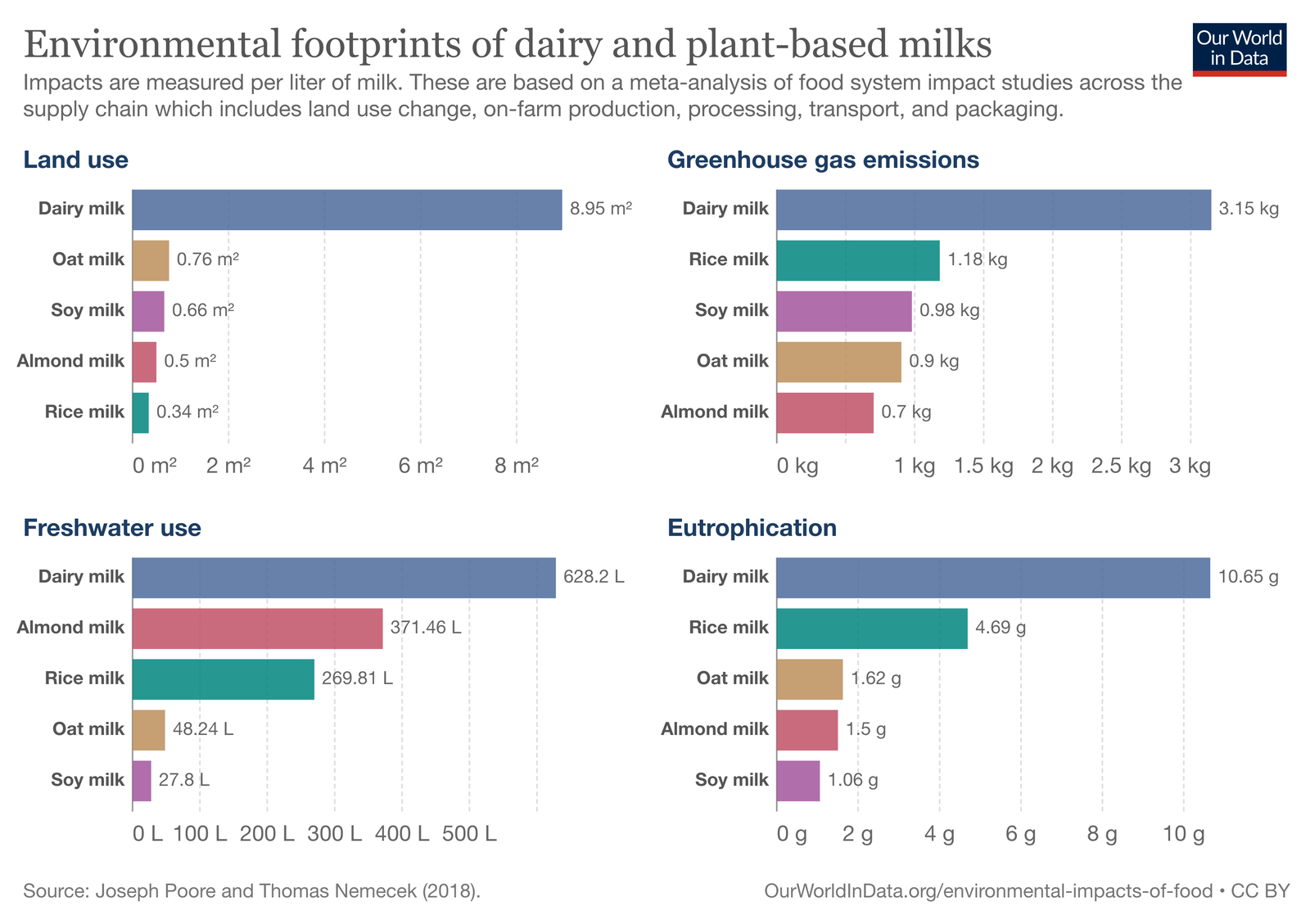
To produce just one litre of dairy milk, 628 litres of water are needed. In comparison, a litre of plant-based milk like almond or oat milk only requires 371 and 297 litres of water, respectively.
However, water usage is not the only environmental issue related to dairy farming. Heavy water usage can lead to manure runoff, which pollutes water sources and harms aquatic ecosystems. And the contamination is not limited to manure; the fertilizers and pesticides used in feed crop production also contribute to water pollution. In contrast, plant-based milk production does not generate manure and relies on plant-based inputs that are less likely to pollute water sources.
Cows naturally produce methane as part of their digestion process, a potent greenhouse gas with a warming potential more than 28 times that of carbon dioxide. Manure is also a source of both methane and nitrous oxide, which is another extremely powerful greenhouse gas. With cows spending most of their lives on factory farms, all the manure is washed off the floors into massive manure lagoons, serving as a massive open-air emissions source.
Plant-based milk, however, has lower emissions compared to dairy milk. Plant-based milk can be derived from a range of crops, and it can frequently be created within the local area, decreasing the emissions that result from transporting goods over long distances. This becomes particularly relevant in lessening the environmental impact of refrigerated transportation, which is indispensable for dairy milk but not for many plant-based milk substitutes.
Figure 1. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers
Source: Poore, J., & Nemecek, T. (2018)
Future Thought Leaders is a democratic space presenting the thoughts and opinions of rising Sustainability & Energy writers, their opinions do not necessarily represent those of illuminem.
Yury Erofeev

Food · Agriculture
illuminem briefings

Sustainable Lifestyle · Food
illuminem briefings

Sustainable Lifestyle · Food
Axios

Food · Sustainable Lifestyle
The Independent

Climate Change · Food
Forbes

Sustainable Lifestyle · Food