Leveraging artificial intelligence in agriculture: transforming the future of farming


· 11 min read
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in agriculture has emerged as a transformative approach to revolutionize traditional farming practices and address complex challenges in the industry. This article presents a comprehensive overview of the applications, benefits, challenges, and future opportunities of AI in agriculture. By harnessing AI algorithms and data-driven models, farmers can optimize resource allocation, enhance productivity, and promote sustainable practices. Precision farming, crop monitoring, yield prediction, pest and disease management, and AI-based irrigation systems are among the key applications of AI in agriculture.
However, challenges such as data privacy, cost, data availability, interpretability, technical expertise, and ethical considerations need to be addressed for successful AI integration. Looking ahead, the future of AI in agriculture holds immense promise, with opportunities for sustainable farming practices, climate resilience, collaborative research, and policy formulation. By leveraging AI alongside human expertise and collaboration, we can shape a future where agriculture thrives, ensuring food security and sustainability for generations to come.
Figure 1. An impression of application of AI devices in a farm

Source: reprint with permission from Instagram @diffused.art]
Agriculture plays a pivotal role in sustaining our growing global population, but it has long grappled with various challenges that hinder its potential to meet the increasing demands for food, feed, fiber, and fuel. With a rapidly growing global population projected to reach 9 billion by 2050, agricultural production must be significantly increased to ensure food security. However, factors such as climate variability, land degradation, water scarcity, and diminishing labor force pose formidable obstacles to achieving this goal.
The integration of AI into agriculture builds upon decades of research and technological advancements. Early AI applications in agriculture focused on rule-based systems and expert systems that attempted to emulate human decision-making processes. However, recent breakthroughs in machine learning, deep learning, and big data analytics have propelled AI to new heights, enabling it to uncover hidden insights and patterns from massive datasets[1,2].
The availability of vast amounts of data from diverse sources, such as satellite imagery, weather data, soil sensors, and crop records, has fueled the growth of AI in agriculture. These data sources, combined with powerful algorithms, enable the development of predictive models, disease detection systems, crop yield estimators, and smart irrigation systems. By leveraging AI technologies, farmers can make data-driven decisions, optimize resource allocation, minimize environmental impact, and ultimately enhance their productivity and profitability.
The convergence of AI with other technologies, such as robotics, drones, and IoT devices, further amplifies its impact on agriculture. Autonomous farming machinery equipped with AI algorithms can perform tasks with precision, reducing labor requirements and increasing operational efficiency. Drones equipped with computer vision capabilities enable rapid and accurate crop monitoring, pest identification, and yield estimation. The interconnectedness facilitated by IoT devices allows real-time monitoring and control of various agricultural parameters, ensuring optimal conditions for crop growth.
As the agricultural sector embraces AI, collaboration between researchers, scientists, farmers, and technology developers becomes crucial. By fostering interdisciplinary partnerships, we can leverage AI's potential to address the pressing challenges facing agriculture and work towards a sustainable and resilient future.
In this article, we delve into the applications, benefits, and challenges of AI in agriculture. We explore how AI is transforming precision farming, crop monitoring, yield prediction, pest and disease management, irrigation systems, and farm machinery automation. Additionally, we examine the importance of data collection and analysis in AI applications and discuss the potential limitations and challenges associated with implementing AI in agriculture. Finally, we shed light on future directions and opportunities for the adoption of AI technologies in the agricultural sector.
AI technologies are being applied across various domains in agriculture, revolutionizing traditional farming practices. Here are some key areas where AI is making a significant impact[3,4]: precision farming, crop monitoring and management, yield prediction, pest and disease management, irrigation systems optimization, and farm machinery automation
Figure 2. Applications of artificial intelligence in the agriculture industry
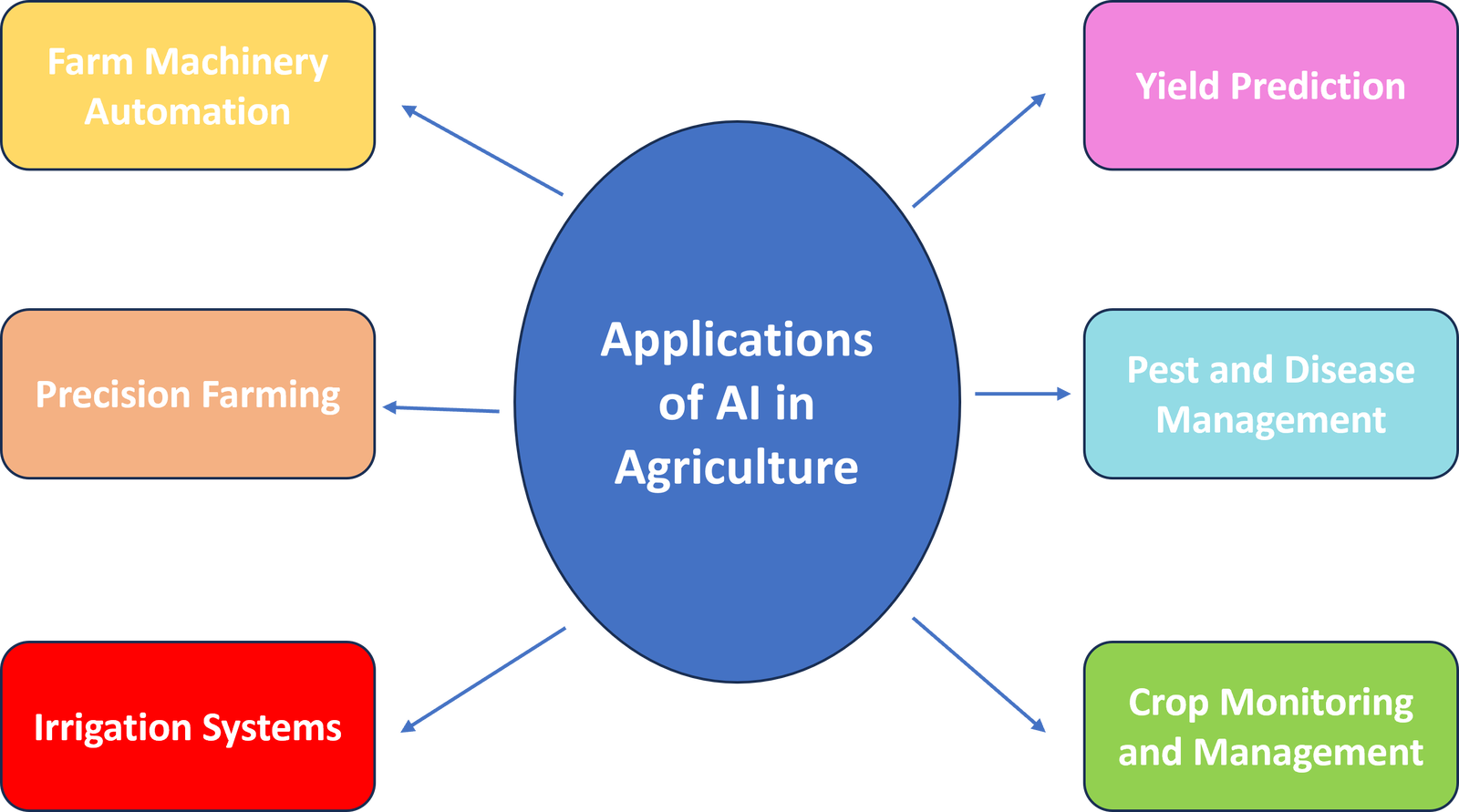
AI enables precision agriculture by integrating real-time data from multiple sources, including satellite imagery, drones, and IoT sensors. Machine learning algorithms analyze these data to provide valuable insights on crop health, soil conditions, and resource requirements. Farmers can then make precise decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pesticide application, resulting in optimized resource utilization and improved crop yields.
AI-powered computer vision techniques facilitate automated crop monitoring and management. Image recognition algorithms can analyze images captured by drones or cameras installed in the field to detect early signs of diseases, nutrient deficiencies, and weed infestations. This enables farmers to take timely action, preventing crop losses and reducing the reliance on chemical interventions.
AI models trained on historical data, combined with real-time environmental and crop data, can accurately predict crop yields. By considering factors such as weather conditions, soil health, and agronomic practices, AI algorithms provide valuable insights into expected harvest volumes. This information helps farmers optimize marketing strategies, plan storage and transportation logistics, and manage supply chain operations effectively.
AI algorithms can identify and classify pests, diseases, and weeds based on visual cues and symptom analysis. By leveraging computer vision techniques and deep learning algorithms, AI systems can provide early detection of potential threats to crops. This enables farmers to take targeted preventive measures, such as precision spraying or localized interventions, reducing the need for broad-scale pesticide applications.
AI-based irrigation systems utilize data from sensors, weather forecasts, and soil moisture measurements to optimize water usage. Machine learning algorithms analyze these data to determine optimal irrigation schedules, ensuring that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time. This promotes water conservation, minimizes water stress on plants, and enhances overall water use efficiency.
AI technologies are revolutionizing farm machinery by enabling automation and autonomous operations. Robotic systems equipped with AI algorithms can perform tasks such as planting, harvesting, and crop monitoring with high precision and efficiency. This reduces labor requirements, increases operational efficiency, and improves overall productivity.
Figure 3. Future AI farming scenario [4]
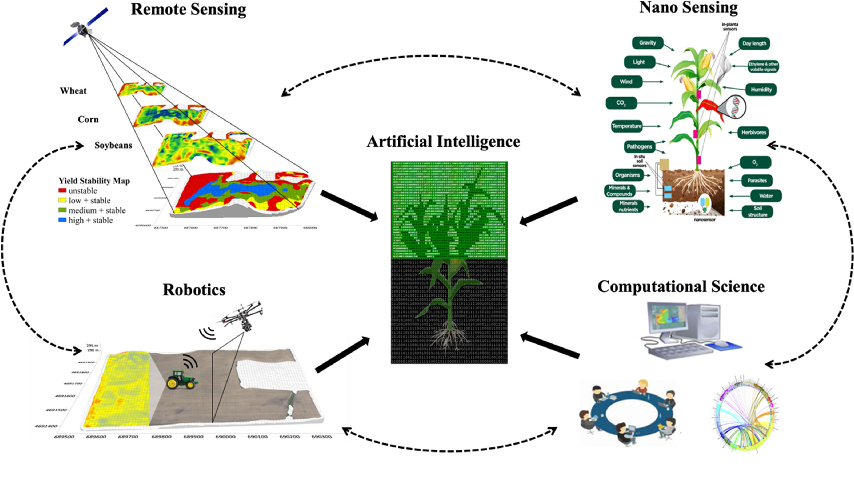
These applications of AI in agriculture demonstrate the transformative potential of this technology in addressing critical challenges and optimizing various aspects of farming operations. However, the successful implementation of AI relies heavily on the quality and availability of data, access to advanced computing resources, and effective integration with existing agricultural practices.
While AI offers immense potential in transforming agriculture, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed [5]:
Figure 4 shows [6] shows the market share and key players in artificial intelligence in agriculture space. The future of AI in agriculture is promising, with several key areas offering significant opportunities:
Figure 4. Artificial intelligence in agriculture market: key players and market size [6]
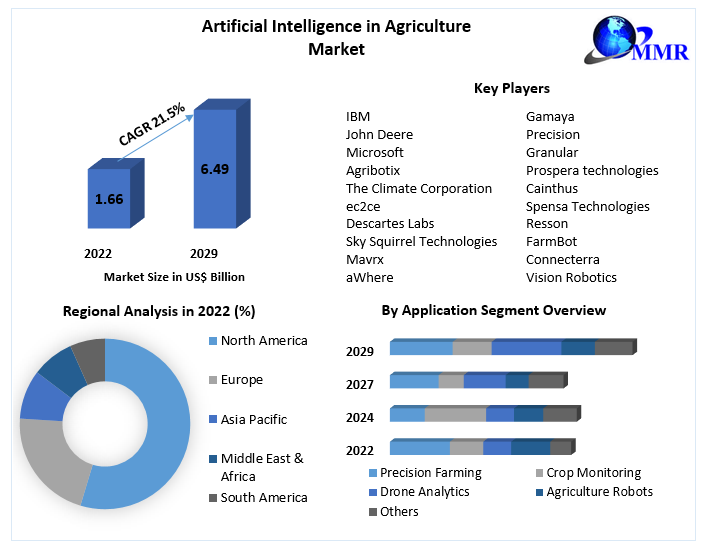
In conclusion, the integration of AI in agriculture represents a transformative opportunity to address the pressing challenges of food security, resource optimization, and sustainability. By harnessing the power of AI, we can create a more efficient, productive, and resilient agricultural sector.
However, careful consideration of ethical, social, and environmental aspects is essential to ensure that AI is deployed responsibly and for the benefit of all. By leveraging AI alongside human expertise, we can shape a future where agriculture thrives, and the needs of both people and the planet are met.
Remember, AI is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and its success lies in its effective integration into existing agricultural practices and systems. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and a forward-thinking mindset, we can harness the potential of AI to build a sustainable and thriving agricultural sector for generations to come.
illuminem Voices is a democratic space presenting the thoughts and opinions of leading Sustainability & Energy writers, their opinions do not necessarily represent those of illuminem.
illuminem briefings

AI · Ethical Governance
illuminem briefings

AI · Corporate Governance
Vincent Ruinet

Power Grid · Power & Utilities
The Economist

AI · Ethical Governance
CNBC

AI · Corporate Governance
Nikkei Asia

Green Tech · Ethical Governance