· 6 min read

Linking Global Sustainability Initiatives with Companies’ Supply Chain Digital Transformations Using Data Science
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 objectives established by the United Nations to address global challenges.
These goals were introduced in 2015 to tackle poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, peace and justice.

For analytics and supply chain professionals, integrating these goals into their operational frameworks is not just a moral imperative but also a great opportunity to boost innovation and efficiency.
In this article, we will explore the essence of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and understand how supply chain analytics can play a key role in achieving them.
💡
Summary
I. What are the Sustainable Development Goals?
1. People
2. Planet
3. Prosperity
4. Peace & Partnership
II. Data Science Can Support SDGs
1. Food Supply Chain Network Design
2. SDG-driven Budget Planning
III. Conclusion
What are the Sustainable Development Goals?
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) symbolise a call to action to create a better world by 2030.

s they cover a wide range of issues from poverty to environmental sustainability, major corporations hold a huge responsibility in the capacity of achieving these goals.
Are you including these goals in your company’s digital transformation?
We will first briefly introduce these 17 goals before focusing on actual business cases using advanced analytics in the next section.
People-oriented goals
The SDGs begin with a focus on people with the goal of improving the quality of life for all.
The first five goals address the most basic human needs
- No Poverty: Eradicate poverty in all its forms everywhere
- Zero Hunger: Achieve food security and improve nutrition
- Good Health and Well-being: Ensure healthy lives and well-being for all
- Quality Education: Secure inclusive and equitable quality education
- Gender Equality: Achieve gender equality and empower all women
International corporations can support these goals by committing to pay fair wages and ensuring the supply of their products to isolated areas.
They can also invest in community development projects such as educational programs, infrastructure improvements and health initiatives.
Planet-oriented goals
The second group is dedicated to the planet emphasizing environmental sustainability.
These goals include
- Clean Water and Sanitation: Availability of water and sanitation for all
- Responsible Consumption and Production: Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns.
- Climate Action: Take urgent action to combat climate change
- Life Below Water: Conserve and sustainably use marine resources
- Life on Land: Promote the sustainable use of forests
Manufacturing companies can invest in the modernisation of their facilities to reduce resource wastage, transition to renewable energy sources and reduce the footprint of their building.
The ultimate goal is to minimize the environmental impact of their activity.
Ideally, some companies can reach carbon neutrality and even positively contribute to wildlife conservation.
Prosperity-oriented goals
The prosperity-focused goals aim to create triumphant societies.

This set includes
- Affordable and Clean Energy: Access to sustainable energy for all
- Decent Work and Economic Growth: Inclusive and sustainable economic growth to provide decent work for all
- Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: Resilient infrastructure, inclusive and sustainable industrialization by fostering innovation
- Reduced Inequality: Reduce inequality within and among countries
- Sustainable Cities and Communities: Create safe, resilient and sustainable cities
The business world can contribute by creating a more inclusive work environment and boosting innovation.
By aligning its operations with Prosperity-Oriented Goals, your company can demonstrate that responsible business practices can lead to sustainable economic growth.
Peace and partnerships-oriented goals
The goals of peace and partnerships are dedicated to fostering peaceful societies and building solid partnerships.
❓ Do you want to know more about ESG scoring?
People-oriented goals: food supply chain network design
Data analytics can aid in achieving these goals by locating areas with high poverty levels and optimizing the supply chain to support them.
Let us consider the example of a food company FoodCorp that would like to contribute to the poverty alleviation of a specific country.
FoodCorp has launched an initiative “Feed the Future” which aims to address People-Oriented SDGs goals.
The objective is to redesign its supply chain network to secure food distribution for remote areas considering
- Bad road conditions that affect transportation lead times
- Specificity in the distribution network (small street shops vs. supermarkets)
- Lack of logistic infrastructure (warehouses, local distribution centres)
- The environmental impact of the network (CO2 emissions)
Which analytics tools can be used to support this project?
For this kind of complex business case, you have a range of tools to support your network design.
You can start with geocoding combined with public databases (population, infrastructure) to analyze the demand per location.
The results can be used with Graph Theory to visualize the connection between retail locations, distribution hubs and demand barycenters.
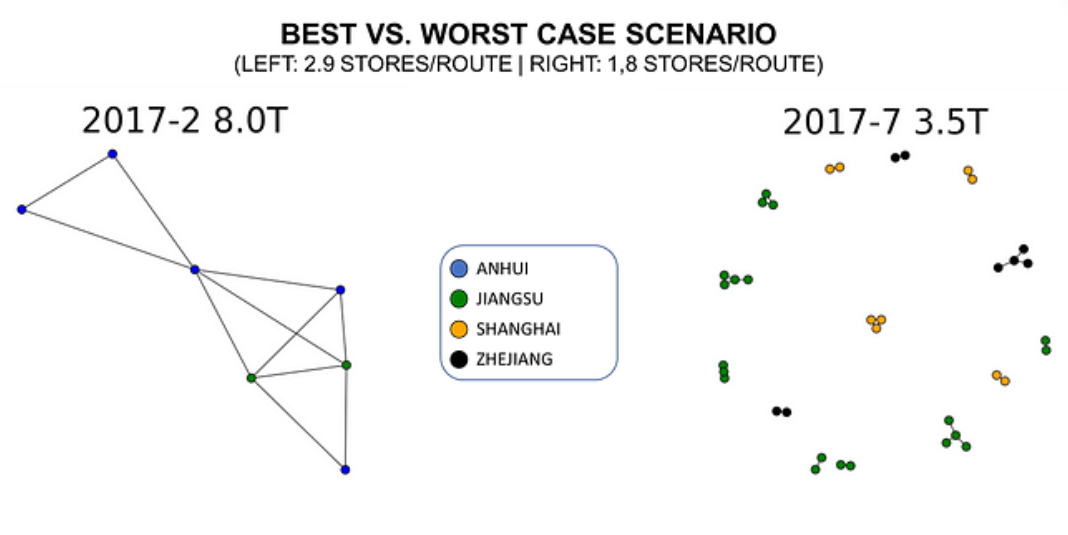
Linear Programming with Python can then help you select the right manufacturing and warehouse locations to ensure optimal distribution operations.
After the network design, you can use optimization algorithms based on the capacitated vehicle routing problem to orchestrate the last-mile delivery considering the road conditions.
This end-to-end supply chain optimization study provides insights on how to ensure the supply of all remote areas at the lowest costs in a sustainable way.
Planet-oriented goals: SDG-driven budget planning
Let’s move to another scenario of an international logistics company operating in four different regions.
The CEO would like to invest in projects supporting the local governments in reaching these five goals.
Regional Directors receive budget applications from their warehouse managers covering the next three years.
How can we allocate our budget to support Sustainable Development Goals?
For each application, the manager provides
- A project description (recruitment, equipment purchase, renovation, …)
- Yearly budget for the next three years ($/Year)
- Return On Investment = Savings — Costs
- Non-financial benefits impacting business development, productivity, ESG indicators or Sustainable Development Goals
Using linear programming, we can automate the process of selecting the projects that will
- Maximize the ROI
- Respect constraints on minimum SDG-driven investments
FIGURE
The objective is to build a balanced budget and avoid spending all the CAPEX on business development (Goal 8) or cost reductions.
For instance, the constraints can be
- ≥25% of the budget must be allocated to Industry Innovation
- At least $1M should be invested in reducing inequalities
This kind of tool can help you to simulate several scenarios and see the impact of strategic targets on future profitability.
Data scientists and continuous improvement engineers can use these advanced tools to collaborate and boost the SDG-driven business transformation of their company.
V. Conclusion
The SDGs, while globally focused, are deeply relevant at a specific industry or company level.
By linking these goals with our supply chain transformation, we not only contribute to a more sustainable world but also unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation.
As supply chain and analytics experts, our knowledge combined with the power of data science can play a significant role in ensuring a brighter future for all.
This article is also published on the author's blog. illuminem Voices is a democratic space presenting the thoughts and opinions of leading Sustainability & Energy writers, their opinions do not necessarily represent those of illuminem.






