Who should pay for carbon removal?


· 4 min read
Carbon removal is necessary to stabilize temperatures along with massive emission reductions. Governments will need to pick up most of the bill. Still, corporate support can play a very important role in catalyzing CDR and other climate solutions, getting new technologies off the ground, and scaling projects that otherwise would not grow. Today, most companies are not contributing nearly as much as they could.
In a new report published by Carbon Gap, Eli Mitchell-Larson and I explore how corporate funds for CDR and wider climate action can be scaled up.
“We find that companies with the lowest emissions can generate the most money for climate.“
We find that companies with the lowest emissions can generate the most money for climate. Both in relative and absolute terms. In the report, we look at a subset of the world's biggest companies, finding that firms generating around 15% of emissions generate 85% of profits. Many of them make profits between $10,000 to $100,000 per tonne of CO2 emitted. The inverse is also true, companies causing around 85% of emissions collect only 15 % of profits. This illustrates the limitations of the polluter pays principle for financing external climate solutions.
There is a wide gap between what companies can afford and what they are willing to pay for external climate solutions like carbon removal. The companies’ ability to pay depends on their profits per ton emitted and the internal investment needs they have to reduce their own emissions. Companies that can reduce their emissions through investment or purchase decisions should do so as a priority. But typically, companies with high profits and a low emission intensity have fewer such opportunities. These companies have enough money implement a credible internal carbon fee and use the money to fund climate projects like carbon removal.
The potential for impact is immense. Over $27 billion could be generated for climate yearly if just 141 high-profit companies (the number we analyzed) spent $100 per ton they emit, representing a small share of their profits. This is 2-3 times more than the total spend on global climate philanthropy annually and 13 times more than the value of the voluntary carbon market. However it is only a small share of the investments needed for the green transition.
The fair share of corporate climate change contributions varies depending on the context. Some companies can afford to pay more than others. To compare climate efforts, contributions can simultaneously be evaluated as a percentage of revenues, percentage of profits, and absolute dollar amount per ton of CO2 emitted. What looks ambitious from a particular angle (for example, looking at a high internal carbon price) might look more modest when viewed as a share of profits. And inversely, a company with a low spend per ton they emit might be a market leader when viewing it as a share of revenue.
This is shown with real data in the graph below, the ones paying a high price per ton emitted are not necessarily the leaders when it comes to contributions as share of profit or revenue, and vice versa. The graph also illustrated how relatively low ambitions are today and how much headroom there is to raise them.
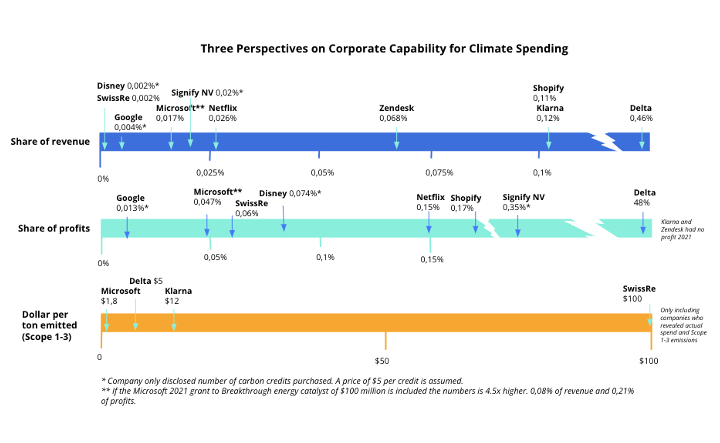
The bar should be raised. Most companies can radically increase their climate support without undermining profitability. High-ambition corporates should embark on an “arms race” to outdo one another.
We can all play a part in making this happen. Executives can increase climate spending, pressure suppliers, and make their companies more transparent. Customers and employees can ask for more climate ambition and openness. Policymakers can create tax incentives, set standards, disclosure requirements, and monitor green claims made by businesses to enhance corporate action. Together, we can help bridge the ambition gap.
Illuminem Voices is a democratic space presenting the thoughts and opinions of leading Sustainability & Energy writers, their opinions do not necessarily represent those of illuminem.
illuminem briefings

Carbon Removal · Carbon
illuminem briefings

Carbon Removal · Net Zero
illuminem briefings

Biodiversity · Carbon Removal
Carbon Herald

Carbon Removal · Corporate Governance
ESG Today

Carbon Removal · Sustainable Finance
World Economic Forum

Carbon Removal · Sustainable Investment